The Impact of IT on Supply Chain Management: A Business proposal of Using IT to improve Supply Chain for Fresh Food Online Retailing
2.4 Digitalised Supply Chain (DSC)
3.2 Applications of Big Data analytics
3.3 Applications of Blockchain
3.4 Application of Digital Supply Chain (DSC)
1.0 Introduction
With the rise of information technology, information flows are becoming increasingly more efficient in supply chain and allow companies to make more timely decisions on their supply chains. The age of industry 4.0 is incoming that arouses a new wave of technological revolutions and innovations. Technologies of industry 4.0 include Cyber-physical systems (CPS), the Internet of Things (IOT), industrial IOT, cloud computing, cognitive computing and AI. These technologies are promised to evolve the efficiency of supply chain. Digital supply networks consist of synchronised planning, connected customer, smart factory, intelligent supply, digital development and dynamic fulfilment. These technologies can be used to improve the supply chain of fresh foods.
In China, most products and services have been exploited by online retailing giants including Alibaba Group, JD Mall and Meituan Delivery. However, the demand for fresh food delivery has been underserved due to supply chain issues. In China, the demand is large and still exploding (Zhuoqiong, 2020). Especially with the breakout of COVID-19, Chinese consumers are unwilling to go outside to purchase fresh food (Zhuoqiong, 2020). Meanwhile, the demand for middle-end and high-end sea food has been growing, with the rise of new middle-class populations. Consumers consider that high-end sea food has great nutritive value and contribute to health. They also strongly believe that food can improve body and mental health (Allison, 2018). Meanwhile, sea food is viewed as social status quo and they have habits to purchase high-end sea food is for special occasions and gift-giving (Gies, 2018). However, it hard for some consumers to access high-end fresh food such as wagyu beef and Boston lobster. They have to visit local sea food market which is likely to be far. With the rise of fast lifestyle, the demand for fresh food delivery is booming.
Many online retailing giants have tried to expand into fresh food segment, whereas their entrepreneur was not successful because three major problems of online retailing fresh food: 1) inaccurate demand prediction; 2) trust issues of customers; and 3) high costs caused by transportation and wastes. It is hard for online retailers to accurately predict demands, thus causing surplus and shortage. The issue also forces online retailers to increase the prices of fresh foods. The second issue is that customers are unwilling to trust quality and security of fresh foods. The third issue is that the inefficiencies of a supply chain causes high wastes and thus increase costs. However, big data analytics, blockchain and digital supply chain can be used to solve the three problems. With the rise of these technologies, the business opportunities have emerged.
The purpose of this paper is to discuss the impact of Information Technology (IT) on supply chain management for fresh food in online retailing segment. The paper discusses a business proposal that uses big data analytics, blockchain and digital supply chain to solve difficulties of online retailing fresh food so as to grasp the exploding demand. The paper starts with the discussion of existing theories and knowledge related with those technologies and supply chain management and then justify the business proposal.
2.0 Literature Review
2.1 Just-In-Time Philosophy
Just-In-Time (JIT) philosophy, developed by Toyota, improves the efficiency and effectiveness of a supply chain by minimising inventories. In the perspective of philosophy, an effective supply chain delivers the right materials or products with right amount to right place at right time (Black and Hunter, 2003). In the theory, minimising inventory is an effective approach to rise efficiency and reduce costs.
2.2 Big Data Analytics
Big data analytics currently is uprising in supply chain management, whereas many companies have realised the significant impact of big data analytics on the effectiveness of decision-making in supply chain management. Big data analytics can be used to analyse the demands, needs and behaviour of customers (Leveling, Edelbrock and Otto, 2014). More importantly, big data analytics is used to optimise Supply Chain Visibility to address complexity and to help decision making on risk management throughout supply chain. Awwad et al. (2018) illustrate that big data significantly increases information from supply chain management, including manufacturing, logistics and retailing. Big data analytics collects data from all sources of a supply chain and generate relevant information for decision-making. It fosters a proactive decision-making approach that forecasts key opportunities and risks in supply chain.
2.3 Blockchain
Blockchain refers to a decentralised, distributed database maintaining a continuously increasing data (Jabbari and Kamnsky, 2018). It can be used as the platform featuring traceability, information and documentation, which can significantly improve the transparency of a supply chain. In short term, blockchain has potential to affect supply chain (Jabbari and Kamnsky, 2018). However, Jabbari and Kamsky (2018) highlight that there are still challenges of using blockchain to solve supply chain issues. For example, the source visibility of blockchain is considerably high. Competitors can use visibility of blockchain to view supply chain sourcing details. Blockchain essentially can improve data security, whereas it also brings great data security risks.
2.4 Digitalised Supply Chain (DSC)
Garay-Rondero et al. (2019) discuss the new digital supply chains by the implementation and promotion of Industry 4.0. They prove the efficiency and effectiveness of the new Digital Supply China (DSCs). The DSCs can improve efficiency and effectiveness of logistics and supply chain. The DSC is defined as an intelligent, value driven network which take advantage of new methods with technologies and analytics to generate innovative types of revenue and business value, by a centric platform which grasps and maximises the usage of real-time information gained from multiple sources (Garay-Rondero et al., 2019). It means that the DSC is a new network featuring technologies and analytics with the purpose of using innovative approaches to create new revenue and businesses. Furthermore, Sarc et al. (2019) point out that a DSC is an intelligent best-fit technological system on the basis of the capability of addressing massive data and great collaboration and communication through digital infrastructure and networks to support and facilitate interaction between companies. DSC can improve value, accessibility and affordability of an organisation’s service. The core enablers and characteristics of the Industry 4.0 are evolving the essence of traditional supply chain.
Many scholars highlight that the trend of Industry 4.0 is promised to reform the value chain and push a virtual value chain empowered by digitalisation (Srai and Lorentz, 2019 and Ye and Ma, 2018). The major characteristics of the DSCs are more accelerated, adaptable, smarter, transparent, internationally connected, scalable and clustered that traditional supply chain. More importantly, the DSCs can solve traditional supply chain’s issues of lacking multi-dimensional model. However, the multi-dimensional model of the DSCs allows a graphical visualisation of the interconnection and fast response between all parties in the chain (Barata et al., 2018). It means that the DSCs can reduce the negative impacts of graphical distance on supply chain and increase the interconnectivity, response and collaboration between all parties of a supply chain (Ganji et al., 2018).
One characteristic of a DSC is a multi-dimensional, non-linear interaction among all of parties and activities in the network, which can improve collaboration and response. Furthermore, a DSC can generate more accurate information of customer needs and demands to timely and fast adapt to quality and quantity needed to be satisfied by digitalisation (Hofmann and Rüsch, 2017). A DSC can effectively and accurately indicate real demand by real-time information and data analytics (Sarc et al., 2019). It also provides new emerging flows sharing including real time information, risk flows, and so on. It can cover the new parties into supply chain management, including 4thparty logistics providers. More importantly, a DSC enables users to integrate other supply chains by clusters, improve interconnection in real time by global connectivity, thereby optimising flexibility and responsiveness (Hofmann and Rüsch, 2017). By a DSC, a company can build a centric platform which grasps and maximises virtual and physical value creation, because the DSC enables the company to develop a virtual and physical global value chain. A DSC also enables companies to provide customised products and services, by data mining and data trends (Srai and Lorentz, 2019). It allows companies to collect a large amount of data and thus predict customer requirement lifecycle so as to adapt their needs and wants. The DSC adopts computational intelligence to form machine-learning bots which are characterised by self-learning, self-regulation and self- creation of decision-making models (Schniederjans, Curado and Khalajhedayati, 2019). The DSC allows companies to stimulate demands, adapt to demands, sense and manage demands so as to continuously improve performance and reduce risks. Furthermore, the DSC can increase a company’s transparency, ethic conducts and accountability (Sundarakani, et al., 2019). It provides a platform for a company to continuously conduct innovation by technologies of industry 4.0 (Tang and Veelenturf, 2019). Companies can use the DSC to use more advanced technologies in the future, as the DSC is a digitalised platform.
As figure 1 shows, the DSC consists of many elements, which can be categorised into six dimensions. The first dimension of the DSC is a clear visualised intelligent technological system, which realises the effective management of the digital and physical DSC management components (Schniederjans et al., 2019). This dimension integrates a company’s all managerial methods. The second dimension links the physical and digital supply chain network structure to the physical and digital supply chain management processes. The third dimension focuses on the implementation and digitalisation of the Industry 4.0 concepts, technologies and characteristics (Ghobakhloo, 2018). It supports R&D activities, improved marketing and production strategies, and innovative types of distribution and delivery. The fourth dimension refers to flows including material, product, services, information, knowledge, funds and risks. The fifth dimension emphasises on information functioning, involving data collection and analytics (Farooque et al., 2019). The sixth dimension is to provide a new lifestyle, business environment and a system integrating real and digital worlds (Calatayud et al., 2019).
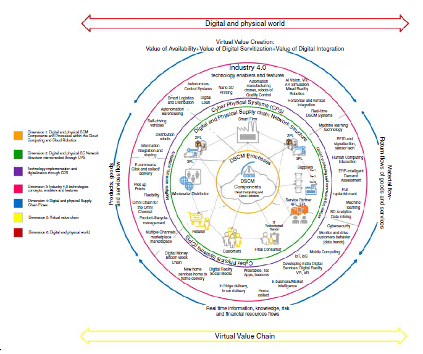
Figure 1: Digital Supply Chain (DSC)
(Source from: Garay-Rondero et al., 2019)
3.0 Business Proposal
3.1 Business Idea and Model
The business proposal is to use a digital supply chain (DSC) that addresses supply chain issues of online retailing fresh food and improve efficiency and cost reduction. The proposal is to focus on middle-end and high-end fresh food market of China. The DSC covers blockchain, big analytics and other important Industry 4.0 enablers and concepts. By using these technologies, a new business can fully achieve the vision of JIT philosophy. Even though currently there are many challenges to apply these technologies, the business currently should focus on the concept of the Industry 4.0.
The business philosophy is to use a DSC to link reality and online to offer more efficient, value-based, transparent and responsible services of fresh good delivery. As figure 2 shows, the business model relies on the DSC consisting of APP, Suppliers, logistics and community stores. The new business only uses an App to sell products and collect feedback and orders. The information is delivered to big data centre that can predict customer demands, needs and behaviour in future. Then, big data centre delivers the order information to suppliers who offer data to logistics providers. The providers transport products to community stores that temporarily stores for a while. They can se deliver men to deliver products to customers. The short distance delivery should take 10 to 30 minutes, which can ensure the food safe and quality. The new business develops small stores in upscale communities of Tier I cities and use those stores to link offline and online. These stores do not sell products but allow customers to visit to show its transparency.
The core of the supply chain is the App can collect customer data for demand prediction and also show information about products, logistics and opertation of community stores in real time to users. The blockchain links the app, suppliers, logisitcs and community stores, and the app provides informaiton to custoemrs. The big data analytics is used to predict each individual customer’s demands, needs and behavour and estimate the deamnd of a whole community.
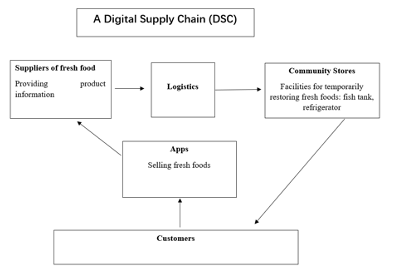
Figure 2: the DSC of the new business
3.2 Applications of Big Data analytics
The new business will use big data analytics to solve the first pain point of fresh food supply chain. Digital technologies can improve efficiency of supply chain, which have the potential to evolve fresh food e-commerce. For e-commerce, online retailing fresh food has three pain points. Firstly, it is hard for online retailers to predict demands, which can cause surplus or shortage. Thus, the prices of fresh foods offered by online retailers are hard to compete with the prices of traditional retailers. The use of big data analytics can solve the first pain point. Big data analytics can be used in fresh foods e-commerce, which will be very effective. Currently, e-commerce cannot properly sell fresh foods such as meat, sea foods and fruits because they cannot predict customer demands. At present, many companies are urgent to develop an e-commerce platform focusing on fresh foods for mainland China. But none of them has succeed including Alibaba Group’s Hema Fresh, partly because of logistics issues.
The new business builds community stores and links them with e-commerce, it can use big data analytics to efficiently predict customer demand to reduce wastes. Also, the business can timely make adjustments to its supply chain and make real-time decisions, with the help of Big data analytics. The App should cover an online community for users to share and discuss their fresh food consumption. Thus, the big data analytics can gain customer data from the online community and orders. More importantly, big data analytics can predict each user’s demands and behaviour, which allows the new business to provide customised and personalised services. It links the APP, so the business also can deliver personalised marketing messages to each user.
3.3 Applications of Blockchain
The new business will adopt blockchain to use the second point of online retailing fresh food. The second pain point to online retailing fresh food is transparency. Consumers are unwilling to trust the quality and safety of fresh food from e-commerce. They pursue high quality and desire to ensure fresh food security. Fresh food is different with groceries because it easily corrupts. Blockchain can improve transparency of fresh food, thus helping online retailers to gain trust from customers.
The new business partners with IBM to develop its own blockchain. Currently, IBM offers mature food trust blockchain solution that improves transparency, trust and newfound collaboration (IBM, 2020). The blockchain links the app, suppliers, logistics, and community stores. Customers can acquire real-time information about their purchase and products by the app. Suppliers take responsibilities of providing real-time product information.
3.4 Application of Digital Supply Chain (DSC)
The new business will adopt a DSC encompassing big data analytics and blockchain to solve the third pain point. The third pain point is low efficiency and high wastes. Fresh food such as sea food is expensive, whereas the wastes increase the costs of online retailers. The new business can use the DSC to solve the problem of wastes and improve efficiency, thus reducing costs.
The DSC enables the new business to accurately demands and predict customer behaviour and demands and to make efficient and effective manual decisions and also machine decisions. It means that big data analytics can make machine decisions autonomously, so the new business only need a few of supply chain managers so as to largely save managerial costs.
4.0 Conclusion
It estimates that the new business requires over 20 million investment for technological infrastructure and software. However, it also is expected that the business can cover the investment soon. The technological advantages can be transferred into customer value including fast delivery, great food quality and freshness. Thus, the business can furtherly develop its brand image and identity. It has strong competitive advantages including high margin, low operating costs (high efficiencies and minimum of wastes), high-end services and great transparency.
The paper discusses the business proposal that uses big data analytics, blockchain and digital supply chain to solve difficulties of online retailing fresh food so as to grasp the exploding demand. From the literature review, this paper finds that technologies of Industry 4.0 can evolve supply chain. A DSC has more advantages in term of efficiency, information sharing and flow, cost control, interconnectivity, and collaboration. Thus, the new business is to use the DSC that addresses supply chain issues of online retailing fresh food and improve efficiency and cost reduction. The DSC covers blockchain, big analytics and other important Industry 4.0 enablers and concepts. These technologies can offer the business great competitive advantage. The future of the business is promising.
Reference
Awwad, M. A, Kulkarni, P., Bapna, R. and Marathe, A. (2018) Big Data Analytics in Supply Chain: A Literature Review, Conference: IEOM International Conference, At Washington DC, USA
Barata, J., Rupino Da Cunha, P. and Stal, J. (2018), “Mobile supply chain management in the Industry 4.0 era: an annotated bibliography and guide for future research”, Journal of Enterprise Information Management, Vol. 31 No. 1, pp. 173-192.
Black, J. T. and Hunter, S., L. (2003). Lean Manufacturing Systems and Cell Design. Society of Manufacturing Engineers.
Ganji, E.N., Coutroubis, A. and Shah, S. (2018), “DCM 4.0: integration of Industry 4.0 and demand chain in global manufacturing”, 2018 IEEE International Conference on Engineering, Technology and Innovation, ICE/ITMC 2018 – Proceedings, pp. 1-7
Gies, E. (2018) The Consequences of China’s Booming Demand for Seafood, [online] Available at: < https://www.hakaimagazine.com/news/the-consequences-of-chinas-booming-demand-for-seafood/> [Accessed on 10 April 2020]
Jabbari, A. and Kamnsky, P. (2018) Blockchain and Supply Chain Management, [online] Available at: <http://www.mhi.org/downloads/learning/cicmhe/blockchain-and-supply-chain-management.pdf >. [Accessed on 2 April 2020]
Leveling, J., Edelbrock, M. and Otto, B. (2014) Big Data Analytics for Supply Chain Management, Conference: The IEEE International Conference on Industrial Engineering and Engineering Management
Ye, Q. and Ma, B. (2018), Internet and Electronic Business in China: Innovation and Applications, Emerald Publishing Limited
 English
English Chinese
Chinese